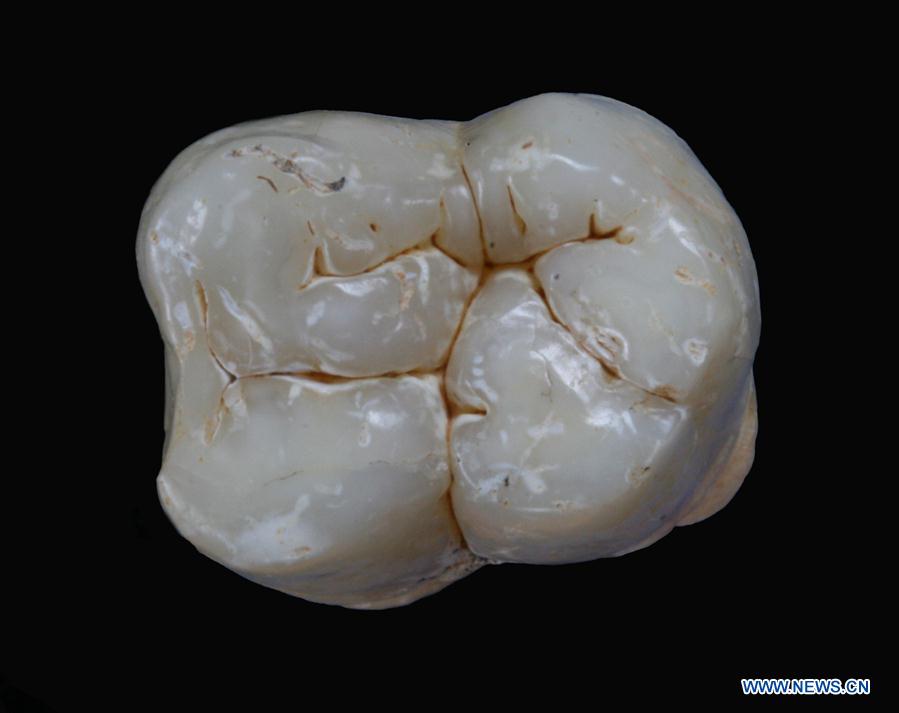
Undated file photo shows a 1.9-million-year-old Gigantopithecus blacki molar found in a cave in Tiandong County of south China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Chinese and Danish scientists have successfully retrieved genetic materials from a 1.9-million-year-old fossil of Gigantopithecus blacki, a species of great ape. The finding, published in a paper on the journal Nature on Wednesday, marks the first time that such ancient protein evidence from fossils in the subtropics was retrieved. Scientists said it sheds new light on the origins and evolution of the long-extinct great ape species. (Xinhua)
NANNING, Nov. 14 (Xinhua) -- Chinese and Danish scientists have successfully retrieved genetic materials from a 1.9-million-year-old fossil of Gigantopithecus blacki, a species of great ape.
The finding, published in a paper on the journal Nature on Wednesday, marks the first time that such ancient protein evidence from fossils in the subtropics was retrieved. Scientists said it sheds new light on the origins and evolution of the long-extinct great ape species.
With the evidence, scientists are able to demonstrate that Gigantopithecus is a sister clade to orangutans with a common ancestor about 12 million to 10 million years ago, implying that the divergence of Gigantopithecus from Pongo forms part of the Miocene radiation of great apes, according to the paper.
Presumed to be more than two meters tall and weigh over 300 kg, giant apes are the largest primates known to have lived on earth. Their fossils date from two million to 300,000 years ago.
The genetic materials -- dental enamel proteome sequences -- were retrieved in 2018 from a 1.9-million-year-old Gigantopithecus blacki molar found in a cave in southern China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, said Liao Wei, a researcher with the Anthropology Museum of Guangxi and a co-author of the paper.
Wang Wei, a professor at Shandong University, said the thick and hard enamel of the great ape and the fact that the fossil was found in a cave with a relatively stable temperature and humidity were both favorable factors for the preservation of the fossil.
"The two factors combined have helped researchers retrieve genetic materials from the enamel of the great ape fossil and make a breakthrough in the research," said Wang, whose team unearthed the fossil in 2008.
It was the first time such ancient genetic materials had been found in a warm and humid environment, said Frido Welker of the University of Copenhagen, the paper's lead author, adding that the finding is groundbreaking in the field of evolutionary biology.















